The challenge of AWS cost optimization is navigating the complexities of cloud environments. Teams must address high expenses and intricate management needs that can impact performance and workflow. This requires consideration of costs, development pipelines, and operations to ensure that every stage of cloud development is optimized efficiently.
This guide will show you how to transition from a reactive approach to proactive cost optimization strategies.
Summary of key AWS cost optimization concepts
Before getting into the technical details, let’s briefly outline the concepts covered in this guide.
| Concept | Description |
|---|---|
| AWS Pricing Models | AWS offers five pricing models: on-demand, reserved, spot, savings plans, and dedicated hosts with discounts of up to 90%. The right selection depends on workload predictability and commitment tolerance. |
| EC2 Instance Rightsizing | Rightsize EC2 instances to match workload needs. Use the AWS Compute Optimizer for recommendations, migrate to Graviton instances for 20–40% better performance, and enable auto scaling groups to adjust capacity. |
| S3 Storage Optimization | Matching data to the right storage class allows you to optimize S3 storage. Use Standard for frequent access, Standard-IA for infrequent use, and Glacier for archives. |
| EBS Storage Optimization | Optimize EBS storage by right-sizing volumes and using GP3 to balance cost and performance. Monitor usage with CloudWatch and remove underutilized volumes. |
| Data Transfer and Networking Cost Optimization | You can reduce data transfer costs by keeping workloads in the same availability zone to avoid cross-AZ fees. Use Amazon CloudFront to cache content closer to users. Replacing NAT Gateway routing with VPC Endpoints enables private access to AWS services. |
| Cost Allocation and Monitoring | Implement mandatory tagging strategies and use tools like CloudBolt to track spending by project, team, or environment. Automated alerts prevent budget overruns. |
| AWS Disaster Recovery | Align AWS disaster recovery with your RTO/RPO goals. CloudBolt automates remediation and manages spend across Backup and Restore, Pilot Light, Warm Standby, and Multi-Site Active/Active approaches to ensure clear cost tracking. |
| AWS Organizations and Shared Resources | Apply SCPs to control actions, consolidate shared infrastructure with shared VPCs and transit gateways, and centralize logs for compliance. Share resources via the Resource Access Manager and standardize setups with Service Catalog to cut costs. |
| Automation & Policy-as-Code | CloudBolt automation enforces governance and embeds compliance across AWS deployments. It removes unused assets and applies policy as code to maintain tagging compliance and control costs. |
Give developers and platform teams the speed they need without losing visibility or governance. Explore how CloudBolt enables faster provisioning, self-service, and unified management across AWS environments.
Why AWS cost optimization is an engineering discipline
AWS cost optimization requires proactive engineering that considers cost at every step. It is not just a financial task but a matter central to how cloud systems are designed and run. Beyond finances, cost optimization helps you avoid overspending on unused resources and maximizes AWS efficiency.
An engineering discipline requires practice through FinOps, guardrails, and automation. FinOps provides engineers with cost insight to balance speed, quality, and spend. Guardrails, like service control policies (SCPs), set cost-aware decisions as the default, and automation supersedes manual reviews, which are unsustainable at scale.
The pillars of cost optimization
In this section, we will discuss each key pillar that forms the foundation of sustainable AWS cost optimization and how they interconnect with your overall cloud strategy.
AWS pricing models and cost drivers
There are five AWS pricing models. The right one for your team depends on your workload requirements:
- On-demand instances work on a pay-as-you-go model. You’re billed only for what you use, with no upfront payment required, and you can terminate at any time. This model is ideal for short-term or unpredictable workloads and is the preset model for most AWS users because you can use it to experiment or get started. However, while it offers numerous benefits, it is expensive, and the cost can add up if used at a large scale.
- Savings plans require you to commit a dollar amount per hour, providing coverage for 1-3 years and offering discounts of about 72%. This option is more flexible and simpler than reserved instances, making it suitable for teams with dynamic workloads.
- Spot instances offer better discounts (approximately 90%) over on-demand instances. They are suitable for users with robust and scalable workloads, akin to CI/CD pipelines or batch jobs. Spot instances may end without prior notice, but you’ll receive a two-minute warning before termination.
- Reserved instances give a discount of up to 72% for a commitment of 1-3 years. Payment options include no upfront, all upfront, or partial upfront. They are easier to manage but lack flexibility: Once committed, you can’t reverse any change. They are ideal for long-running, stable workloads.
- Dedicated hosts provide your organization with access to physical servers managed by AWS, eliminating operating costs. Commonly used by large enterprises that have existing software licenses and need total control, dedicated hosts are more expensive than other models.
Learn how to set up an actionable AWS chargeback program with real-world strategies from Cloud Finance experts.
EC2 cost optimization through rightsizing
Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) instance rightsizing is a method of picking an instance type that delivers the performance for your workload without paying for excess capacity.
You can start with the AWS Compute Optimizer. It reviews your resource usage and recommends the best fit for your workload. For example, if an EC2 C5.2xlarge instance is running at just 15% CPU, downsizing to a C5.xlarge reduces costs by half.
For higher efficiency, consider migrating to Graviton-based instances (e.g., C6g, M6g, and R6g). They provide a 20–40% better price-to-performance ratio for workloads such as web and application servers.
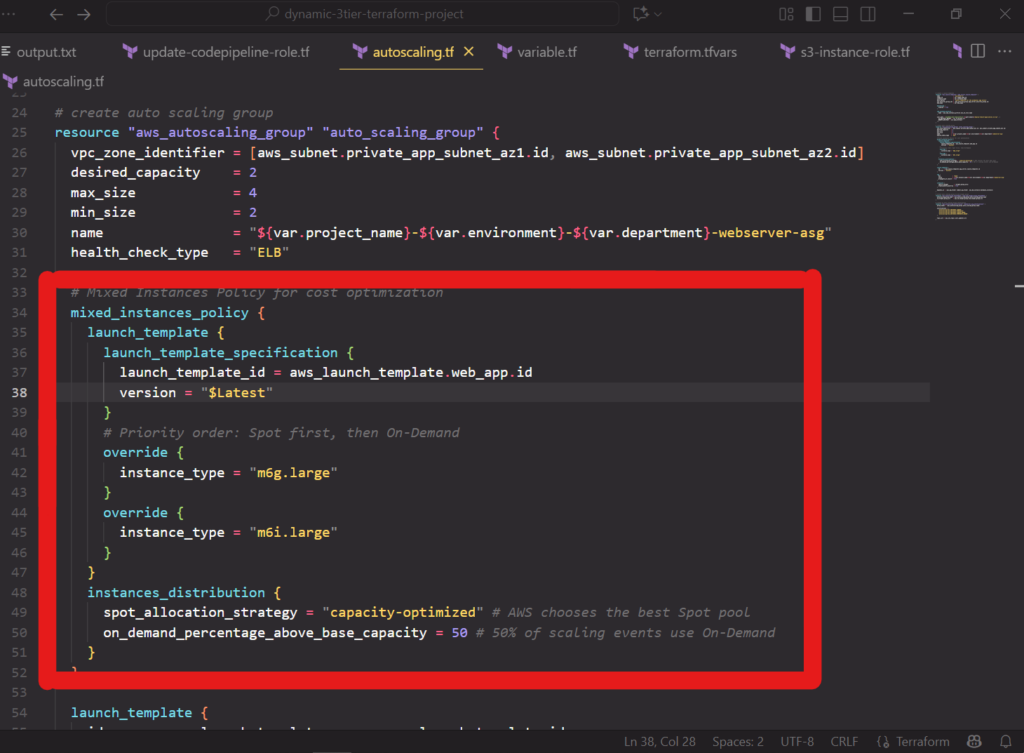
You can add automation and use auto scaling groups (ASGs) to scale up your EC2 fleet during busy periods and down when demand is low. These methods make rightsizing a dependable strategy.
For greater savings, you can also configure a mixed instances policy within your ASG to launch a combination of on-demand and spot instances. This can help maximize savings.
S3 storage optimization: intelligent tiering and lifecycle management
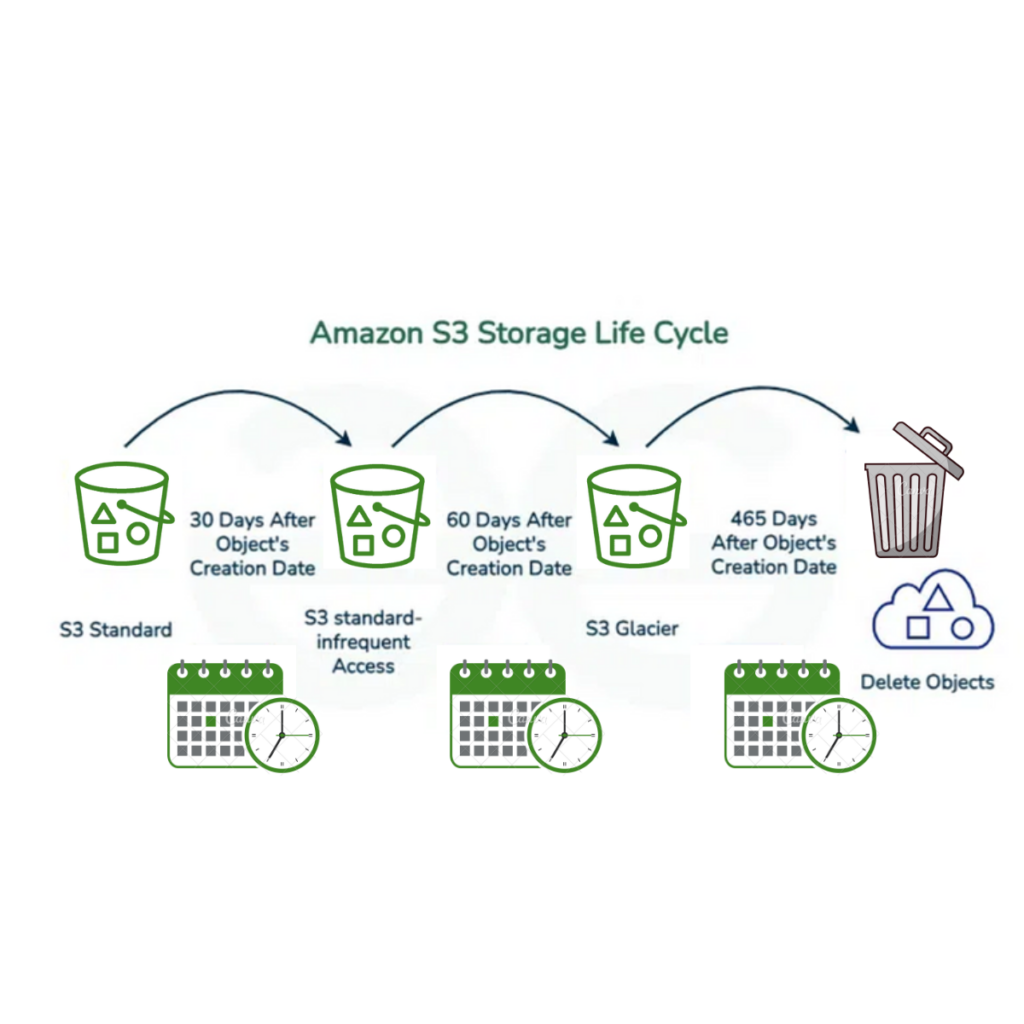
S3 storage optimization involves organizing your data in Amazon S3 so that storage costs align with usage and avoiding having objects in expensive storage tiers stay longer than expected, which can incur unnecessary costs. You can optimize costs by selecting the S3 storage class that matches your data’s access pattern: Standard for frequent access, Standard-IA for infrequent access, and Glacier for archives. Making the correct choice prevents you from overpaying for storage resources you aren’t using.
| Storage Class | Cost (Storage Per Month) | Retrieval Fee | Min Billable Object Size | Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standard | $0.023 per GB | N/A | – | Used for storing data you see often |
| Standard-IA | $0.0125 per GB | Per GB retrieved | 128kb | Stores data you still need but seldom access |
| Glacier or Glacier Deep Archive | $0.000099 per GB | Per GB retrieved | 40kb | Stores long-term data that’s rarely retrieved. |
Intelligent tiering moves objects between access tiers based on usage patterns and is best used when you can’t predict how often data is accessed. If combined with lifecycle management rules, you will be able to transition objects to cheaper storage over time.
EBS storage optimization: right-sizing and snapshot hygiene
Elastic Block Store (EBS) is a block storage service for AWS EC2. To optimize your EBS storage, start with a volume that is the right size. You can utilize general-purpose AWS EBS volumes (GP3) to adjust input/output operations per second (IOPS) and throughput for improving performance. IO1/IO2 are best for workloads that need guaranteed performance.
Monitor volume usage with CloudWatch and scale down underutilized EBS volumes to prevent waste, and use Data Lifecycle Manager or AWS Backup to manage snapshots. A key part of this strategy is applying backups selectively; for example, you can skip creating snapshots for temporary resources, such as test instances or build servers, mainly if the data can be regenerated. For long-term retention over a year, configure Data Lifecycle Manager to archive snapshots to lower-cost storage.
Keeping old snapshots and unattached volumes is a typical source of waste. Ideally, you want to automate snapshot and volume cleanup by finding unattached EBS volumes and removing them using Lambda or AWS Systems Manager (SSM) automation to prevent unnecessary costs. SSM automation can also run predefined tasks across instances.

Data transfer and networking cost optimization
Data transfer and networking cost optimization involves cutting the costs of moving data across networks in a cloud environment.
To minimize data egress, keep data within the same availability zone (AZ) or region. Group application tiers that communicate to each other in the same AZ to avoid cross-AZ transfer fees. You can also use Amazon CloudFront to cache content closer to users. By doing so, you reduce the load on your origin servers and reduce data transfer from services.
Another primary source of costs is routing traffic through a NAT gateway to access AWS services. To eliminate charges, make use of VPC endpoints for private connections that bypass the public internet. For instance, gateway endpoints are functional for S3 and DynamoDB, and interface endpoints are used for other services.
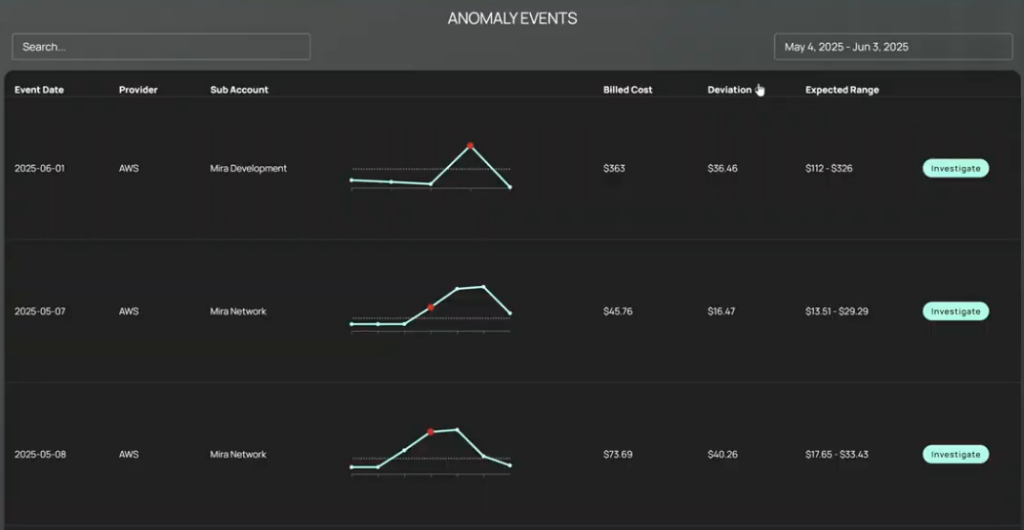
Identify cost hotspots with the cost and usage report in Amazon Cost Explorer. You can group and filter costs by usage type, including data transfer or NAT gateway bytes, to find significant cost drivers.
Achieving visibility: cost allocation and monitoring
Cost visibility means measuring and understanding spending on cloud services. There is a need for a solid tagging strategy that is applied from the start of a project, which ensures that every resource is properly labeled from development to production. Although AWS provides native tools, platforms such as CloudBolt offer more insights and automation. Here’s how:
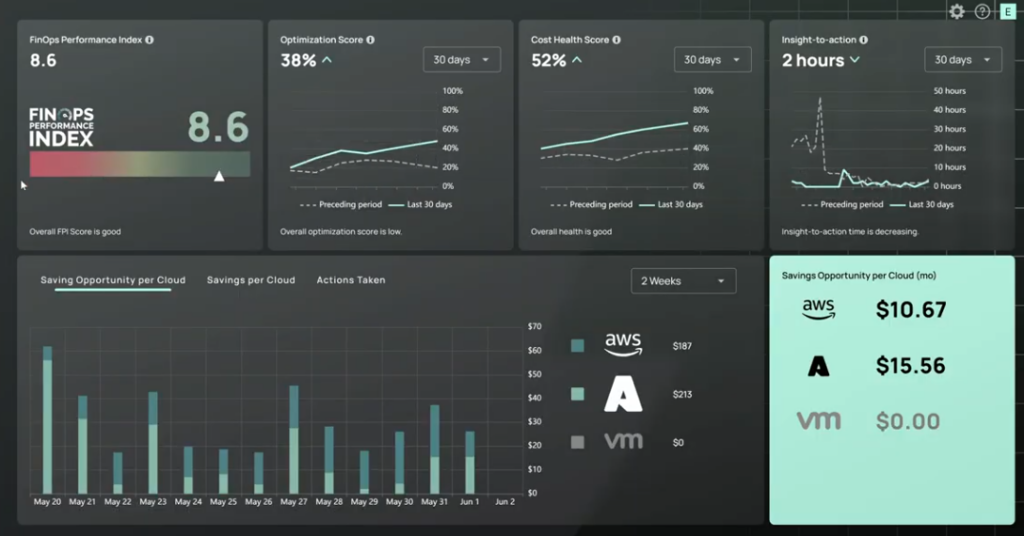
- Enhanced visibility with CloudBolt’s optimization dashboard: The dashboard offers a clear and intuitive view of your cloud resources, and it also helps you note idle assets using native AWS tools. The dashboards provide cost-saving recommendations based on their usage; the visualization gives direction on rightsizing instances and optimizing storage.
- Implementing a mandatory tagging strategy with CloudBolt: The tool extends beyond AWS tagging by enforcing tags across hybrid and multi-cloud environments. The platform applies essential tags when provisioning resources, which means that every resource is identified from the start to prevent costs from being overlooked. It also detects noncompliant resources and runs automated workflows to correct tagging.
- Advanced budget management and incident detection: CloudBolt enhances AWS budget management by providing visibility and alerts. It monitors your budgets and sends notifications through Slack or email. It can detect unusual spending patterns and trigger automated workflows to contain costs.
- Automating governance with CloudBolt: CloudBolt’s policy engine includes governance automation on top of AWS Config. It enables you to monitor compliance from a single dashboard and benefit from creating custom policies that align with your organization’s cost and operational rules. For instance, you can set schedules to turn off non-production workloads during nights and weekends, which is a simple way to reduce unnecessary runtime charges. Additionally, you can set up automated workflows that resolve issues without requiring manual intervention.
- Unified cost visibility: You can monitor multiple accounts and cloud environments on Cloudbolt, which consolidates costs and chargebacks for internal allocation. It also supports dashboards for different stakeholders and merges visibility with automation, enabling organizations to implement proactive cost optimization.
AWS disaster recovery
A good disaster recovery (DR) strategy should align with your recovery time objective (RTO) and recovery point objective (RPO) requirements without overspending. CloudBolt’s Optimization Dashboard and automation capabilities improve these AWS DR approaches by continually optimizing cost and automating remediation. While AWS offers different strategies, CloudBolt allows you to keep them cost-effective:
- Backup and Restore: Back up data to a separate region and rebuild infrastructure when needed. CloudBolt monitors backup storage costs and ensures that lifecycle policies move old backups to cheap storage classes.
- Pilot Light: Keep a minimal version of your core application running in a standby region. CloudBolt’s Waste Signals detects oversized DR resources and recommends right-sizing.
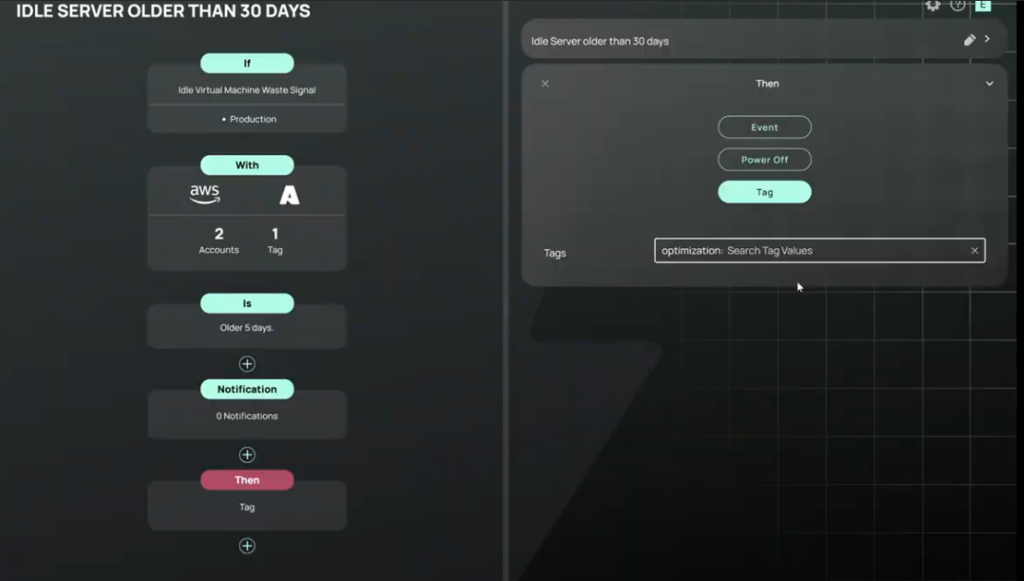
Warm Standby: Run a scaled-down version in the standby region. CloudBolt’s policy engine can scale it up during tests or disasters, then scale it down later to reduce costs.
- Multi-Site Active/Active: Maintain active environments across multiple sites to ensure high availability and reliability. CloudBolt provides precise showback/chargeback so business units understand the cost of this highest-availability tier.
AWS Organizations and shared resources
AWS Organizations streamlines large-scale governance. Consolidated billing enables management to merge charges from all member accounts, allowing them to share volume discounts and RI or savings plan benefits.
Service control policies (SCPs) act as guardrails, limiting actions like creating oversized EC2 instances in development or launching resources in expensive regions.
Centralizing shared resources eliminates complexity, avoiding the duplication of costs by consolidating common infrastructure. A shared VPC removes the need for multiple network setups, and a transit gateway connects VPCs and on-premises networks through a single hub. A designated logging account aggregates CloudTrail, CloudWatch, and AWS Config data for a single view of compliance.
AWS Resource Access Manager lets accounts easily share resources, and AWS Service Catalog provides standardized, pre-approved infrastructure templates. With these tools, you reduce the possibility of duplication, which in turn reduces unnecessary spending.
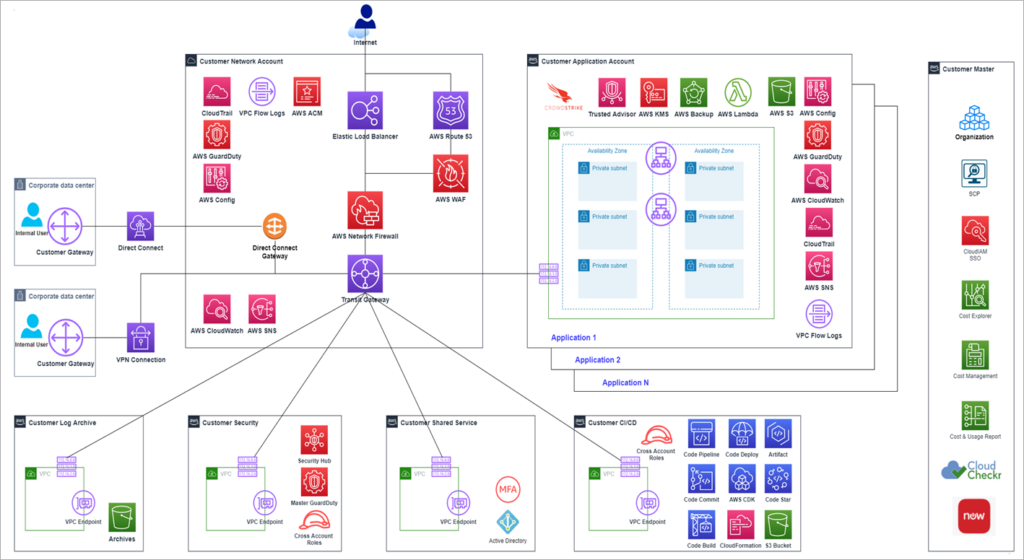
Credit to AWS Image —–
Automation and policy as code
Sustainable cloud savings occur when you enforce standard procedures throughout your infrastructure. CloudBolt’s automation increases AWS capabilities where engineering discipline is essential. It integrates governance and cost control into every deployment. Blueprints can create templates with pre-set configurations, such as Graviton instances and gp3 volumes.
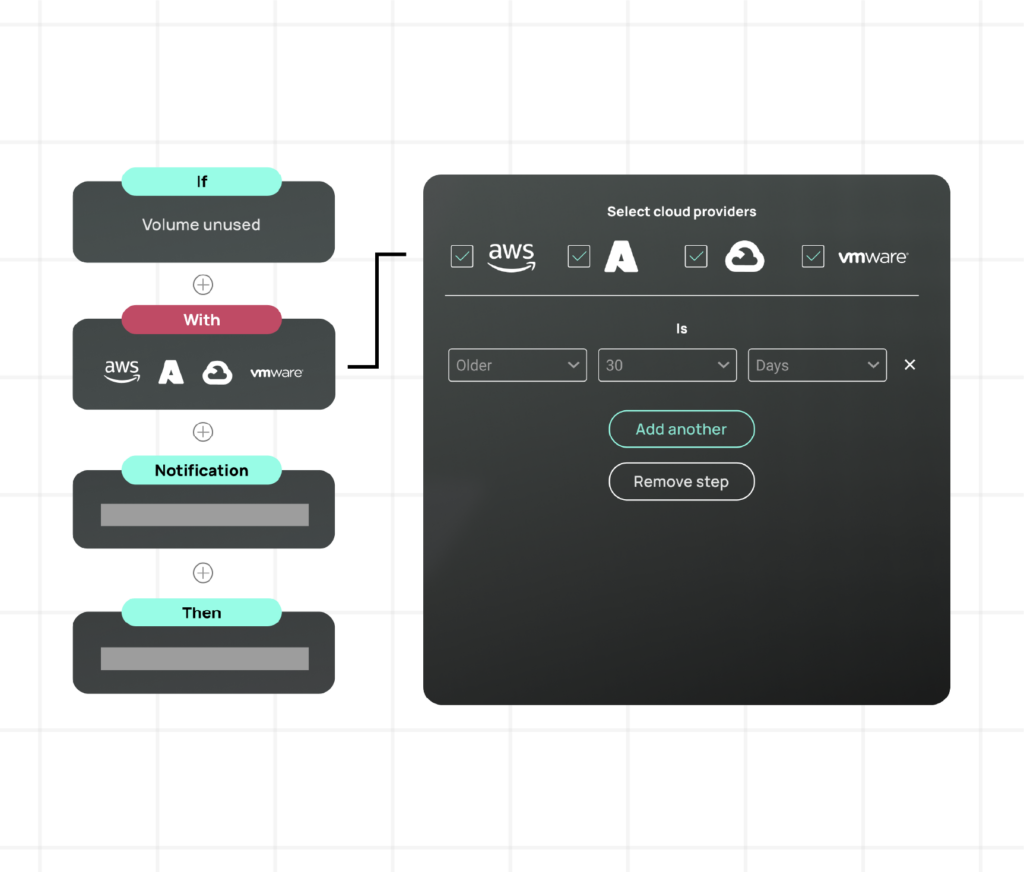
Resource sizing adapts to the environment and scales for development, testing, and production. It reduces the need for manual review and embeds compliance into the infrastructure. CloudBolt’s approach unifies cost management and related features.
Additionally, automated cleanup scripts run on a scheduled basis to identify unused resources and remove them. By doing so, your cloud environment stays lean and costs remain under control.
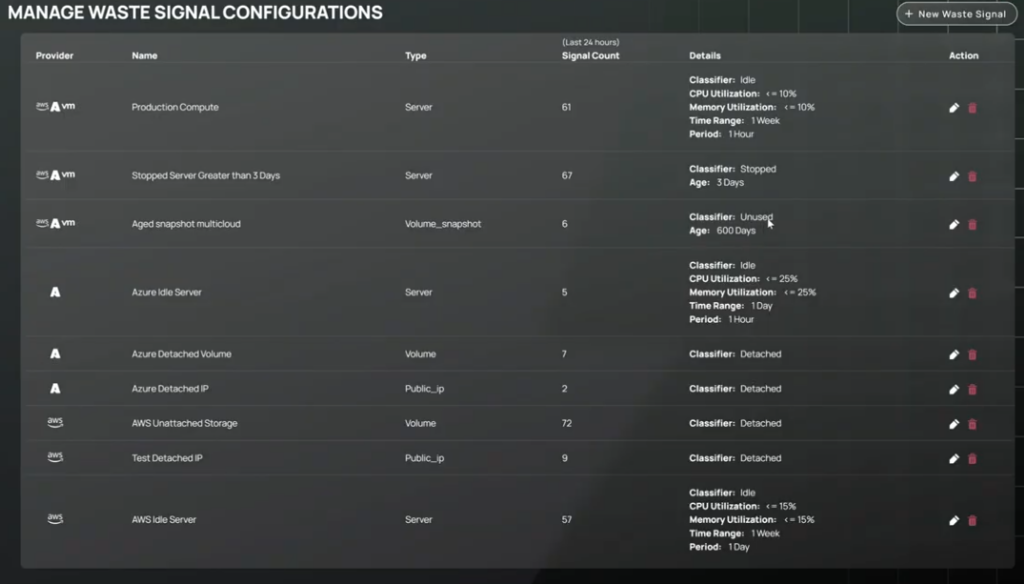
Policy as code with CloudBolt Waste Signals extends governance beyond basic AWS Config rules. It monitors all AWS accounts for tagging compliance and repairs violations. Automated remediation workflows can fix noncompliant resources and connect with CMDB systems to auto-tag them. It makes it easy to track usage and manage cost in your cloud environment.
Conclusion
AWS cost optimization is an ongoing engineering discipline integrated within the FinOps model. Start with visibility and tagging, then dive into rightsizing and purch
Related Blogs
Kubernetes Resource Optimization with Humans in the Loop, with Ray Chen | KubeFM
Watch this Kube FM interview of Ray Chen, Head of SRE at Trumid, as he demonstrates how StormForge helps platform…

