Kubernetes Cost Optimization Tools: Key Categories for Reducing Cloud Costs
Manual Kubernetes cost management becomes increasingly complex as workloads scale and multiply across namespaces. This makes platform engineering teams struggle to monitor resource consumption patterns and optimization opportunities. Today’s Kubernetes systems require specialized tools to analyze, monitor, and automatically adjust resource allocation across dynamic cluster environments.
The cost optimization challenge extends beyond simple monitoring. Organizations typically overprovision Kubernetes resources by 40-60%, creating substantial waste through static resource configurations that cannot adapt to changing application demands. Manual rightsizing approaches fail to keep pace with the velocity of modern deployments, while inconsistent optimization practices across development teams compound cost inefficiencies.
This article examines the essential categories of Kubernetes cost optimization tools and implementation strategies that enable platform teams to build efficient, cost-effective clusters through automated resource management.
Summary of key Kubernetes cost optimization tool categories
| Tool category | Description |
|---|---|
| Resource monitoring and visibility tools | These tools form the foundation of data-driven cost decisions. They monitor actual resource consumption patterns, provide cost attribution across namespaces and teams, and identify optimization opportunities through detailed metrics and dashboards. |
| Automated rightsizing platforms | These tools reduce manual configuration overhead while maintaining performance by analyzing historical usage patterns and automatically recommending or implementing optimal resource requests and limits based on actual workload requirements. |
| Cluster autoscaling solutions | Scaling solutions dynamically adjust cluster size based on resource demand, automatically provision and deprovision nodes to match workload requirements, and optimize node selection for cost efficiency across different instance types. |
| Multi-cloud cost management platforms | These platforms provide unified cost visibility across different cloud providers, compare pricing options, and automate workload placement decisions based on cost optimization criteria and performance requirements. |
| Policy enforcement and governance tools | Policy tools implement automated policies for resource allocation, prevent resource sprawl through quota management, and enforce cost-conscious practices across development teams through guardrails and approval workflows. |
| Spot instance and preemptible VM managers | These products automate the use of discounted cloud instances for appropriate workloads, handle instance interruptions gracefully, and optimize the balance between cost savings and workload reliability. |
CloudBolt delivers continuous Kubernetes rightsizing at scale—so you eliminate overprovisioning, avoid SLO risks, and keep clusters efficient across environments.
Resource monitoring and cost visibility tools
Kubernetes abstracts infrastructure complexity, making it difficult to attribute costs to specific applications, teams, or business units. Traditional cloud billing provides node-level costs but lacks the granularity to understand which workloads drive expenses. Organizations struggle to identify optimization opportunities and implement accountability measures across development teams without proper cost visibility.
Platform teams need tools to break down costs by namespace, label selectors, and custom attribution models. The most effective monitoring solutions provide namespace-level cost breakdown for team-based accountability, label-based cost allocation using Kubernetes metadata for detailed financial reporting, and historical trend analysis to identify seasonal variations and optimization opportunities.
The challenging aspect of Kubernetes cost allocation reporting is avoiding the use of approximations and instead integrating with actual cloud bills, which include negotiated rates, committed usage discounts, and credits, as well as utilizing accurate cost data down to the container level. This article explains the rationale behind Kubernetes cost allocation functionalities designed to address these challenges.
The table below summarizes the essential functionalities of Kubernetes cost optimization tools:
| Required Capability | Purpose | Implementation Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Multi-environment cost visibility | Track costs across Kubernetes, VMs, cloud services, and on-premises infrastructure in unified dashboards | Essential for organizations with hybrid cloud deployments and legacy infrastructure alongside Kubernetes |
| Real-time resource utilization monitoring | Monitor actual CPU, memory, and storage consumption at the pod and container level with sub-minute granularity | Enables identification of optimization opportunities before they compound into significant waste |
| Automated cost allocation and chargeback | Attribute costs to teams, applications, or business units automatically using namespace and label hierarchies | Reduces manual reporting overhead and enables accountability without creating an administrative burden |
| Integration with native cloud billing | Connect directly to AWS Cost Explorer, Azure Cost Management, and GCP Billing APIs for accurate cloud costs | Ensures cost data reflects actual provider charges, including discounts, credits, and commitment-based pricing |
| Historical trend analysis and forecasting | Analyze usage patterns over weeks or months to predict future costs and identify seasonal variations | Supports capacity planning and budget forecasting with data-driven projections |
| Custom tagging and labelling enforcement | Validate that all resources include required cost allocation tags before deployment | Prevents untagged resources that create gaps in cost attribution and reporting accuracy |
| Idle resource allocation and distribution | Allocate shared infrastructure and unused capacity costs across teams and applications to reflect true resource ownership | Critical for environments with variable utilization where significant compute capacity remains unallocated |
Organizations should prioritize tools that provide visibility across their entire infrastructure stack, rather than relying solely on solutions specific to Kubernetes. Hybrid environments with both containerized and traditional workloads require unified cost monitoring to identify optimization opportunities across all resource types.
Cost analysis solutions should not only be holistic but also integrated with capabilities to execute the tasks necessary to implement the optimization recommendations automatically. The challenge with tools that report on cost savings opportunities but can’t execute them is that they provide visibility but don’t reduce the infrastructure costs. Platform engineering teams often find themselves overwhelmed with data but lack automated mechanisms to act on optimization opportunities, resulting in a practical gap between awareness of costs and actual cost savings.
This page serves as a good starting point for learning more about tools that can enforce customizable FinOps policies based on workflows that include four steps: Acknowledge, Assign, Approval, and Action.
Automated rightsizing and resource optimization platforms
Setting optimal resource requests and limits manually becomes increasingly difficult as cluster size grows and application diversity increases. A typical web application might start with conservative resource specifications, leading to systematic overprovisioning that compounds across hundreds of deployments.
Consider this common scenario, where a development team deploys a microservice with these initial specifications:
resources:
requests:
memory: "1Gi"
cpu: "500m"
limits:
memory: "2Gi"
cpu: "1000m"
After analyzing actual usage patterns over several weeks, an automated rightsizing platform might recommend optimized settings:
resources:
requests:
memory: "256Mi"
cpu: "100m"
limits:
memory: "512Mi"
cpu: "200m"
This optimization represents a 75% reduction in memory requests and 80% reduction in CPU requests while maintaining performance headroom based on observed peak usage.
Modern rightsizing platforms use machine learning algorithms to automate this analysis across entire clusters. These tools process historical usage data to identify patterns, account for traffic spikes and seasonal variations, and generate confidence intervals for resource recommendations. Advanced platforms can continuously adapt to changing application behavior without manual intervention. As applications experience organic user growth and evolving usage patterns, automated rightsizing adjusts resource allocations incrementally to match demand. This drastically improves manual approaches, which require repeated analysis and reconfiguration cycles.
StormForge Optimize Live represents the current state of the art in automated Kubernetes rightsizing. The platform uses forecast-based machine learning to analyze workload patterns and predict future resource needs, rather than relying on simple percentile-based calculations from historical data. This approach prevents both overprovisioning during usage declines and underprovisioning during growth periods.
StormForge automatically discovers all workloads across clusters and begins analyzing resource consumption patterns within minutes of deployment. The platform’s machine learning continuously learns from actual usage data to generate optimized recommendations for CPU and memory requests and limits. Organizations typically see 50-70% reduction in cloud costs while simultaneously improving application reliability by eliminating CPU throttling and out-of-memory errors.
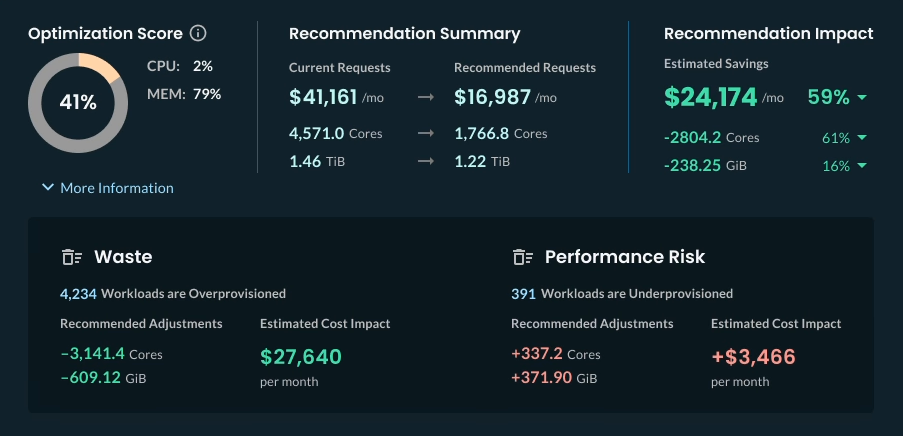
The platform addresses challenging workload types that traditional rightsizing tools struggle with, including Java Virtual Machine (JVM) applications with their unique heap and off-heap memory requirements. When out-of-memory events occur, StormForge’s OOM Response feature automatically increases memory allocations and continues refining recommendations over time, preventing recurring reliability issues without manual intervention. Platform teams can explore these capabilities firsthand through the Optimize Live Sandbox, which provides a live demonstration environment with interactive workload examples and real-time optimization metrics.
Reality Check: Manual rightsizing becomes virtually impossible beyond 50-100 applications. Teams report spending 2-3 hours per application for thorough analysis, making automation essential for larger environments.
Effective rightsizing creates the foundation for efficient cluster operations, but optimal cost management also requires intelligent cluster autoscaling to match infrastructure capacity with actual workload demands.
Cluster autoscaling and node optimization tools
Effective cluster autoscaling requires coordination between pod rightsizing and node provisioning to achieve optimal bin packing and resource utilization. The process involves multiple decision points that traditional tools handle poorly, particularly when dealing with diverse workload requirements and cost optimization objectives.
Here’s a typical implementation workflow for advanced autoscaling:
- Analyze pending pod requirements: Examine CPU, memory, and special hardware needs for pods waiting to be scheduled.
- Evaluate current node utilization: Assess existing nodes for available capacity and consolidation opportunities.
- Select optimal instance types: Choose nodes that best match pending workload requirements while minimizing cost.
- Provision nodes with appropriate policies: Configure nodes with correct taints, labels, and availability zone distribution.
- Monitor and optimize placement: Continuously assess node efficiency and trigger consolidation when beneficial.
- Handle node lifecycle events: Manage spot instance interruptions and planned maintenance gracefully.
The standard Cluster Autoscaler provides basic functionality but has limitations in complex scheduling scenarios. Karpenter for AWS offers more sophisticated node provisioning with just-in-time scaling, intelligent instance type selection based on pending pod requirements, and smart scaledown with Karpenter Consolidation.
Karpenter’s advantages include eliminating node groups entirely, provisioning nodes in under 30 seconds, and automatically selecting from hundreds of instance types. Karpenter can reduce costs by 60-70% for organizations running batch workloads through optimal instance selection and spot instance integration.
Combining automated rightsizing with native Kubernetes autoscaling presents significant challenges that many organizations underestimate. The HorizontalPodAutoscaler (HPA) and VerticalPodAutoscaler (VPA) often conflict when both attempt to scale the same workload simultaneously: HPA adds replicas while VPA modifies resource allocations, creating resource contention and scaling oscillations.
Modern event-driven autoscaling solutions like KEDA provide more sophisticated scaling logic that can more effectively coordinate with rightsizing platforms. KEDA’s external metrics and scaling policies enable more predictable resource management when combined with automated rightsizing recommendations, reducing the conflicts inherent in using multiple native autoscalers simultaneously.
Implementation requires configuring appropriate policies for different workload types. Batch processing jobs may tolerate longer scaling delays in exchange for cost savings, while customer-facing applications require rapid scaling with higher availability guarantees.
This practical FinOps playbook shows you exactly how to build visibility, enforce accountability, and automate rightsizing from day one.
Spot instance and preemptible VM management
Spot instances represent the most significant opportunity for immediate cost reduction, offering 50-90% savings compared to on-demand pricing. A typical organization running a 100-node cluster can reduce compute costs from $50,000 monthly to $15,000-25,000 through strategic spot instance adoption.
The following matrix summarizes the suitability of various workload types.
| Workload Type | Spot Suitability | Expected Savings | Implementation Complexity |
| Batch processing | Excellent | 70-90% | Low |
| Stateless web apps | Good | 50-70% | Medium |
| CI/CD pipelines | Excellent | 60-80% | Low |
| Development environments | Excellent | 70-90% | Low |
| Databases | Poor | N/A | High |
| Real-time APIs | Fair | 30-50% | High |
AWS-specific solutions include the AWS Node Termination Handler for graceful spot instance lifecycle management:
kubectl apply -f https://github.com/aws/aws-node-termination-handler/releases/download/v1.19.0/all-resources.yaml
This handler monitors for spot instance interruption notices and gracefully drains nodes before termination, preventing service disruptions.
Risk mitigation requires implementing automated failover mechanisms that can quickly replace interrupted spot instances with on-demand capacity. Organizations typically maintain 20-30% on-demand capacity as a buffer while still achieving 50-60% overall cost savings and maintaining reliability.
Multi-cloud and hybrid cost optimization
Organizations using multiple cloud providers face exponentially more complex cost optimization challenges. Each provider offers different pricing models, instance types, and optimization tools that require specialized knowledge to use effectively.
Let’s look at an example illustrating typical cross-cloud pricing complexity. Here are some options:
- AWS m5.xlarge: $0.192/hour (4 vCPU, 16 GB RAM)
- Azure D4s_v3: $0.192/hour (4 vCPU, 16 GB RAM)
- GCP n1-standard-4: $0.189/hour (4 vCPU, 15 GB RAM)
While the base pricing appears similar, actual costs vary significantly based on the following:
- Network egress charges (AWS: $0.09/GB, Azure: $0.087/GB, GCP: $0.12/GB)
- Storage pricing models and IOPS limitations
- Reserved instance discount structures and commitment terms
- Spot instance availability and interruption rates
- CPU-to-memory ratios that differ across cloud providers (AWS favors memory-optimized instances; GCP offers more flexible ratios)
Managing costs across multiple cloud providers requires unified approaches that can normalize different pricing models and provide consistent optimization strategies. For Kubernetes-specific approaches, implementing consistent tooling like Prometheus across all clusters and standardizing labeling practices enables cross-cloud visibility without vendor lock-in.
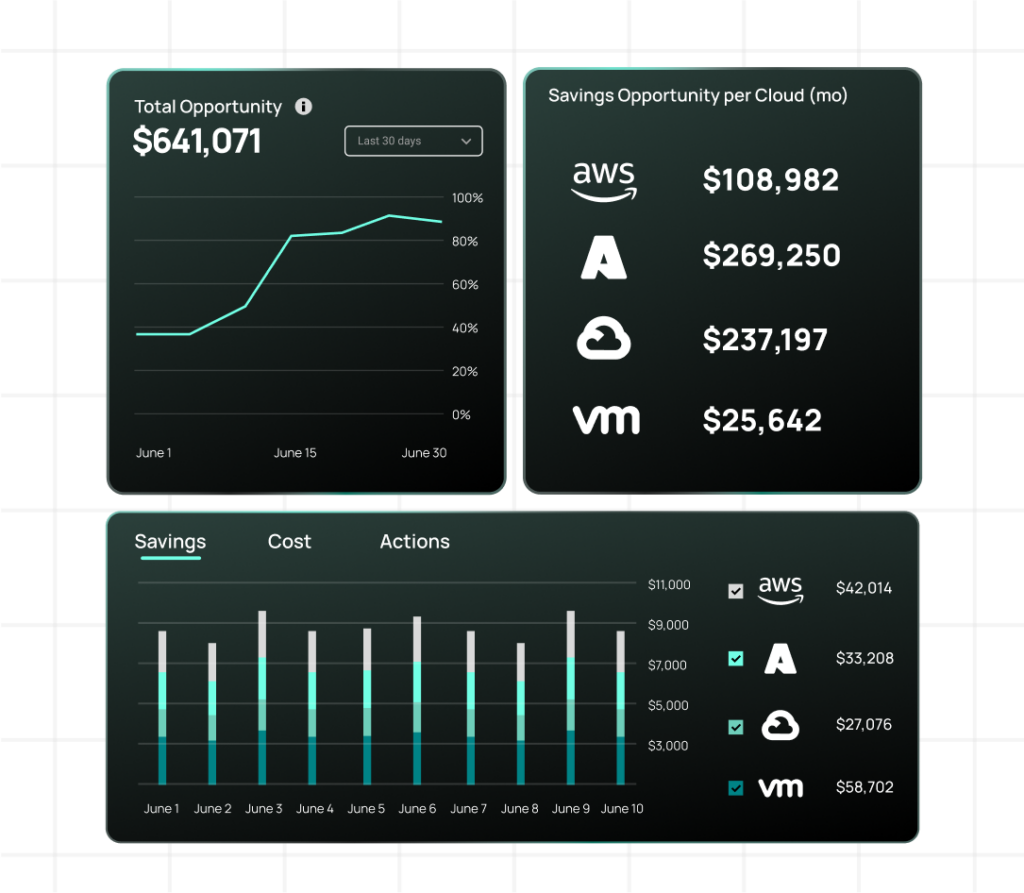
Implementation strategies should develop cloud-agnostic Kubernetes configurations that can be optimized regardless of underlying infrastructure. This approach enables workload portability and cost arbitrage between cloud providers based on current pricing and capacity availability.
Policy enforcement and cost governance tools
Manual cost management becomes ineffective as development teams gain autonomy and deployment velocity increases. Automated policy enforcement ensures cost-conscious practices without creating bottlenecks in development workflows.
Here’s an example Open Policy Agent (OPA) policy that enforces resource limits:
package kubernetes.admission
deny[msg] {
input.request.kind.kind == "Pod"
input.request.object.spec.containers[_].resources.requests.memory
not input.request.object.spec.containers[_].resources.limits.memory
msg := "Memory limits are required when memory requests are specified"
}
deny[msg] {
input.request.kind.kind == "Pod"
container := input.request.object.spec.containers[_]
memory_request := container.resources.requests.memory
memory_limit := container.resources.limits.memory
memory_request_bytes := units.parse_bytes(memory_request)
memory_limit_bytes := units.parse_bytes(memory_limit)
memory_limit_bytes > memory_request_bytes * 4
msg := sprintf("Memory limit %v exceeds 4x memory request %v", [memory_limit, memory_request])
}
This policy prevents deployments with missing memory limits and enforces reasonable ratios between requests and limits, preventing resource waste while maintaining flexibility.
Implementation should start with warning-only policies to assess impact before implementing enforcement. Tiered policies can apply stricter cost controls to development environments while prioritizing availability for production workloads.
Tool selection and implementation strategy
Successful cost optimization requires careful tool selection based on technical requirements and organizational constraints. Platform teams must evaluate solutions that integrate with existing workflows while providing the automation necessary for meaningful cost reductions.
Here’s an example of an implementation timeline with milestones.
Phase 1: Foundation (Weeks 1-4)
- Deploy cost monitoring and attribution tools.
- Establish baseline metrics and reporting dashboards.
- Implement consistent labeling across all resources.
- Identify the top 10 optimization opportunities.
- Train team on cost visibility tools.
Phase 2: Manual optimization (Weeks 5-8)
- Apply initial rightsizing recommendations manually.
- Configure basic cluster autoscaling policies.
- Implement namespace-level resource quotas.
- Establish cost review processes with development teams.
- Measure and document initial cost improvements.
Phase 3: Automation (Weeks 9-16)
- Deploy automated rightsizing platform in monitoring mode.
- Implement advanced autoscaling with spot instances.
- Enable policy enforcement for new deployments.
- Establish continuous optimization feedback loops.
- Scale automation to production workloads.
Organizations typically see 20-30% cost reductions in Phase 2 through manual optimization, with an additional 15-25% improvement in Phase 3 through automation. Total implementation costs are usually recovered within 3-6 months.
Integration with development workflows ensures cost optimization becomes part of existing practices rather than creating separate processes. This includes CI/CD pipeline validation, automated resource recommendation in pull requests, and cost impact analysis in deployment tools.
Best practices and recommendations
Start with comprehensive monitoring to understand current spending patterns before implementing optimization tools. For example, a 500-node cluster might reveal that 60% of costs come from just 20% of applications, enabling targeted optimization efforts with maximum impact.
Use consistent labelling strategies across all resources to ensure accurate cost attribution. Implement required labels for team, environment, application, and cost-center through admission controllers to prevent deployment of untagged resources, as shown here:
kubectl label namespace production cost-center=engineering team=platform environment=prod
Begin automation gradually with non-critical workloads to build organizational confidence. Development and staging environments provide excellent testing grounds for automation without impacting customer-facing services.
Critical Insight: Organizations that implement automated rightsizing report 40-50% reduction in manual optimization effort while achieving 15-20% better cost efficiency than manual approaches.
Establish continuous optimization processes that adapt to changing workload patterns. Cost optimization requires ongoing attention as applications evolve and infrastructure scales. Implement weekly cost reviews and monthly optimization assessments to maintain efficiency gains.
Balance cost optimization with performance requirements to avoid compromising service quality. Use performance testing to validate that optimizations maintain application behavior and establish rollback procedures for any optimization that impacts user experience.
Build organization-wide cost awareness through dashboards that show team-specific resource consumption and costs. Implement cost budgets and alerts at the namespace level to encourage responsible resource usage across development teams.
The airline analogy translates complex cluster economics into language your execs, engineers, and FinOps teams can all understand.
Conclusion
Kubernetes cost optimization tools have evolved from simple monitoring solutions to sophisticated platforms that automatically manage resource allocation, scaling, and placement decisions across complex cluster environments. The most effective approaches combine monitoring, automated rightsizing, intelligent autoscaling, and policy enforcement in comprehensive optimization strategies.
Platform engineering teams should focus on building integrated optimization approaches that start with visibility and progress toward full automation. Success requires implementing these tools gradually while maintaining application performance and development team productivity throughout the optimization process.
As Kubernetes environments continue growing in complexity and scale, automated cost optimization becomes essential for controlling cloud spending. Organizations that invest in proper tooling and optimization processes today—particularly those implementing machine learning-driven platforms capable of continuous adaptation—will be better positioned to scale efficiently as their containerized infrastructure expands and business requirements evolve.
Related Blogs

VMwhere? How Enterprises Decide What Moves Off VMware and Where It Goes Next
Two years into VMware’s Broadcom era, most enterprises aren’t asking whether they are leaving. They’re trying to answer a more operational question. What can move safely this year, what has to wait,…
